Q. What is the need of doing hi-pot test?
A. We are checking that the bus bar is capable of withstanding of high voltage are not.We also say as we are checking dielectric strength of insulation medium for high voltages.
Q. hi-pot test is limited times test,we should not do for more times, why?
A. As we do it many times ,the properties of insulation medium changes and life time decreases.But for bus bars insulation medium is air so we can do any times as air changes generally but consider about supporting structures.
Q. How much voltage should apply?
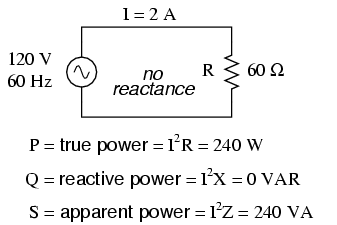
A. assume the bus rated voltage as V volts(ac rms voltage)
The amount of AC voltage applied to cable = ( 2* V + 1)
Q. Why we apply 100% of voltage ,in cable hi-pot we apply only 80% voltage, why?
a. For cables,already at factory they will do hi-pot test at 100% dc voltage,in order to protect life of insulation medium we will reduce applied voltage,if we do same test for third time we will decrease to 60% voltage.
In bus bar,the insulation medium is air,so it will replaced by fresh air so no problem for bus bars.but in case of cables the insulation medium is constant,so its property will change.
Q. Why we applying AC voltage for bus bar, but in case of cable we can apply DC voltage only?
A. The distance between the phases is some what high so capacitance between phases are low,so they will take very low charging currents ,so no problem of capacitance.
PROCEDURE:
1.Remove all external connections before doing test.
2.Connect the remaining phases and to earth.
3.Confirm that no other person is in contact with bus.
4.Apply the AC voltage with using hi-pot kit.
5.Note down the leakage current.
6.Discharge the charge after the test.
7.Repeat the above steps to all cores.
Q. Why we should do megger after the hi-pot?
A. To identify the insulation is same as before hi-pot or not.It was not so important for bus bars as medium was free air,but while considering supporting structures we should take in to account.